HERS (Home Energy Rating System) is a rating system developed by RESNET in order to measure how efficient a home performs. From the RESNET About Us page:
"In April 1995, the National Association of State Energy Officials and Energy Rated Homes of America founded the Residential Energy Services Network (RESNET) to develop a national market for home energy rating systems and energy efficient mortgages.
RESNET’s standards are officially recognized by the federal government for verification of building energy performance for such programs as federal tax incentives, the Environmental Protection Agency’s ENERGY STAR program and the U.S. Department of Energy’s Building America Program."
One of the best explanation of HERS and Home Energy Rating comes from Energy Vanguard. In their definition, they state:
"The home energy rating process basically comprises four parts:
- Assessment of building components
- Diagnostic/performance testing
- Energy modeling
- Reports
Certified home energy raters go through training and certification processes and undergo regular quality assurance."
Your home gets a HERS Index (a.k.a. HERS Score) by a certified home energy rater (find a certified home energy rater here). You would probably get a HERS Score after your certified home energy rater performs a home energy audit. Again, from Energy Vanguard’s Home Energy Rating lingo:
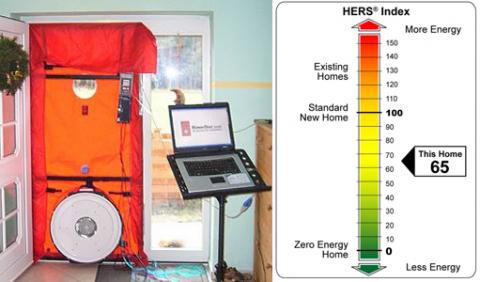
"HERS Index – the official number that comes from the rating. A home that just meets code has a HERS Index of 100. For every point above or below 100, the home is that many % less or more efficient than the same home built to code. For example, a home with a HERS Index of 70 is 30% more efficient than its code-built counterpart. In other words, lower numbers are better. A HERS Index of zero means it’s a Net Zero Home (i.e., it produces as much energy as it uses each year)."
Further explaining the HERS Index is EnergyStar.gov:
The HERS Index is a scoring system established by the Residential Energy Services Network (RESNET) in which a home built to the specifications of the HERS Reference Home (based on the 2006 International Energy Conservation Code) scores a HERS Index of 100, while a net zero energy home scores a HERS Index of 0.
Your HERS Score comes in handy in several places:
- Stand-alone score: By itself, it gives you a good idea of how your home compares to a baseline home. I’m a firm believer that when we have quantitative values to use for comparison we are able to better define how we need to improve. For instance, you can get a certified Home Energy Rater to analyze your home on date 1, then you can make the suggested improvement, and at date 2 you can get your home rated again to see how much your score has improved.
- LEED for Homes: If you want to get a LEED score for your home, like Lorraine and Judd Horalby who we covered in our post on LEED for Homes, then chances are it will utilize the HERS index to help determine what level of LEED status your home will achieve.
- Energy Star for Homes: Energy Star for Homes is different than Home Star (a.k.a. Cash for Caulkers bill) but is yet another energy efficient stamp of approval (just like LEED for Homes is). LEED for Homes is monitored by the U.S. Green Building Council (which actually is not a government program, it is a non-profit) while Energy Star for Homes is a joint project by the U.S. DOE and EPA. The EnergyStar website has a nice summary of the relationship between the HERS Index and Energy Star for Homes: “A home energy rating involves an analysis of a home’s construction plans and onsite inspections. Based on the home’s plans, the Home Energy Rater uses an energy efficiency software package to perform an energy analysis of the home’s design. This analysis yields a projected, pre-construction HERS Index. Upon completion of the plan review, the rater will work with the builder to identify the energy efficiency improvements needed to ensure the house will meet ENERGY STAR performance guidelines.”
As you can see, HERS and the HERS Index (Score) come in handy in several places (yes, I know it gets confusing sometimes). By giving home energy raters a set of standards to measure how efficient a home performs, HERS helps homeowners and homebuilders understand how efficient their home is and how they can improve.
Other Links:

Post new comment